More patients are searching for alternatives to ADHD medication. Is TMS for ADHD the answer?
Since the turn of the 21st century, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) diagnoses have steadily increased—especially among adults. A 2017 study estimates that between 2007 and 2016, diagnoses for adult ADHD patients more than doubled.
And what’s behind this sharp uptick? While genetic factors do play a role (with research indicating that ADHD runs in families) it’s hard to ignore the timing. From 2007 to 2016, smart phones and social media moved into the center of our culture, fracturing our attention spans along the way.
This increase in diagnoses has also encouraged new interest in alternative treatment options, like emotional therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS).
But before we dive into the potential of alternative treatments like TMS, let’s explore the specifics of ADHD.
What is ADHD?
ADHD is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder, characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. If left unmanaged, these neural patterns can make it difficult to function in work, academic, and social settings.
While the exact causes of ADHD remain unclear, a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors is thought to contribute to its development, and neuroimaging studies indicate differences in brain structure and function among people with ADHD.
Common symptoms of ADHD include:
- Difficulty focusing
- Difficulty listening
- Hyperactivity
- Poor organization and time management
- Forgetfulness
- Impulsiveness
Traditional Medications vs. TMS
ADHD is a real psychiatric disorder that is commonly treated with FDA-approved medications like Adderall, Ritalin, Concerta and Vivanse.
ADHD medications augment neurotransmitters, like dopamine and norepinephrine, to help improve symptoms. There are two primary types of ADHD medication: stimulants and non-stimulants. Stimulants augment levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, while non-stimulants increase levels of norepinephrine. BY modulating neurotransmitter activity in the brain, these medications can help enhance attention, focus, and impulse control.
However, not everyone with ADHD responds the same way to medications. It is important to note that finding the right pharmaceutical treatment may require clinician-guided trials with different medications.
To expand treatment options beyond medications like Ritalin and Adderall, researchers and clinicians have investigated alternative therapies such as TMS, which can non-invasively modulate brain activity. But does TMS therapy help with ADHD?
Understanding TMS
TMS is a chemical-free, non-invasive magnetic pulse treatment that stimulates mood regulation. By applying magnetic pulses to targeted areas, TMS treatment can either excite or inhibit neural activity, depending on the parameters used. This innovative treatment has been used to treat various neurological and psychiatric conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and chronic pain.
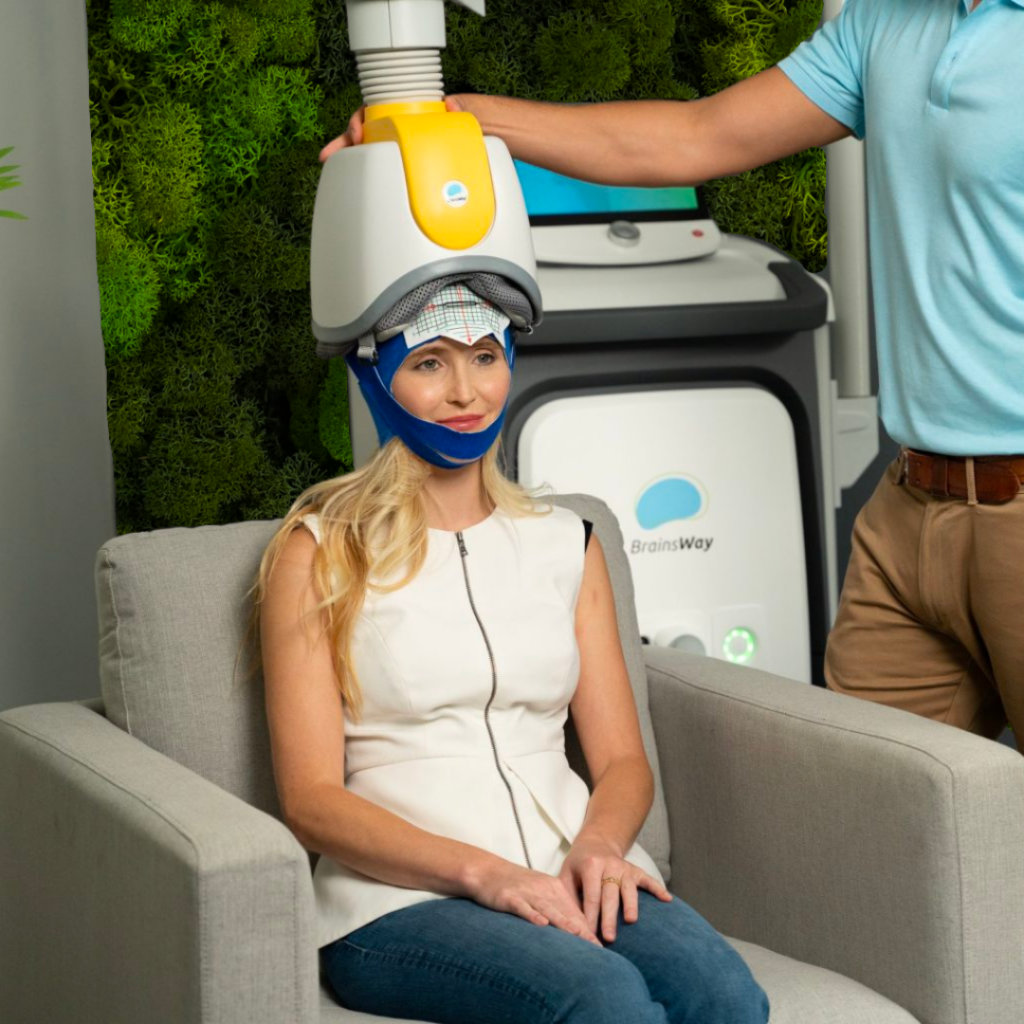

The Promise of TMS for ADHD
The rationale behind using TMS for ADHD lies in its ability to modulate neural circuits implicated in the disorder. Patients who have been diagnosed with ADHD experience dysregulation in frontal-subcortical circuits involved in attention, impulse control, and executive functions. By targeting and modulating these circuits, TMS holds the promise of alleviating ADHD symptoms.
TMS for ADHD: the Research
While the use of TMS for ADHD is still relatively new, there’s growing interest and research in this area. Several studies have investigated the effectiveness of TMS in managing ADHD symptoms, albeit with varying results.
A 2020 study confirmed that TMS applied to the right pre-frontal cortex (which is implicated in ADHD neuropathology) is a safe and effective means of alleviating ADHD symptoms in adults. Similarly, a 2023 study confirmed the therapeutic efficacy of TMS in improving improving sustained attention and processing speed.
While these studies underscore the potential of TMS to gain mainstream recognition as an alternative to ADHD medication, we still need more large-scale clinical trials to solidify its efficacy as a valuable treatment for adolescents and adults with ADHD.
Potential Advantages of TMS
One of the significant advantages of TMS over traditional pharmacotherapy is its non-invasiveness and minimal side effects. Unlike medications, which can cause adverse side effects like insomnia, loss of appetite, and mood changes, TMS is generally well-tolerated and does not involve systemic administration of drugs. For patients who have tried medications in the past and experienced difficulty stomaching the side effects, TMS is an especially attractive treatment option.
Additionally, TMS offers the flexibility of targeting specific brain regions implicated in ADHD, allowing for personalized treatment approaches. By tailoring stimulation parameters to individual neurobiology, clinicians can potentially optimize treatment outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its vast potential, several challenges and considerations need to be addressed before TMS can be widely adopted as a treatment for ADHD. First and foremost, although the FDA has approved TMS to treat depression and OCD, TMS for ADHD is still considered an off-label treatment, which may impact insurance coverage.
And although this therapy is generally well-tolerated, some patients do experience minor discomfort after treatment sessions, including headaches, jaw pain, and discomfort at the site of the pulses. Because of these consideratios, patients should always seek counsel from their doctor or psychiatrist while they explore TMS therapy for their mental health.
The future of TMS for ADHD
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation has demonstrated promising results in modulating neural circuits associated with ADHD. And as more people diagnosed with this mental health condition seek medication alternatives, TMS for ADHD may become increasingly accessible and mainstream.
Patients with ADHD should have more treatment options beyond just medications. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) provides a non-invasive method for achieving significant improvements without the potential side effects of medication. Thus far, research indicates that Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation may effectively modulate neural circuits associated with ADHD.
But in order for TMS to be widely accessible, we still need more robust clinical studies focused on the efficacy and safety of stimulation therapy among both children and adults with ADHD.
References:
Alyagon U, Shahar H, Hadar A, Barnea-Ygael N, Lazarovits A, Shalev H, Zangen A. Alleviation of ADHD symptoms by non-invasive right prefrontal stimulation is correlated with EEG activity. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;26:102206. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102206. Epub 2020 Feb 6. PMID: 32062566; PMCID: PMC7021642.
Faraone, S.V., Larsson, H. Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 24, 562–575 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0